Who we are
Manitoba Hydro, with headquarters in Winnipeg, Manitoba, is one of the largest integrated electricity and natural gas utilities in Canada.
- We are a provincial Crown Corporation (owned by the Province of Manitoba) with $3.04 billion in annual revenue and $31.14 billion in assets (as of the 2021-22 fiscal year).
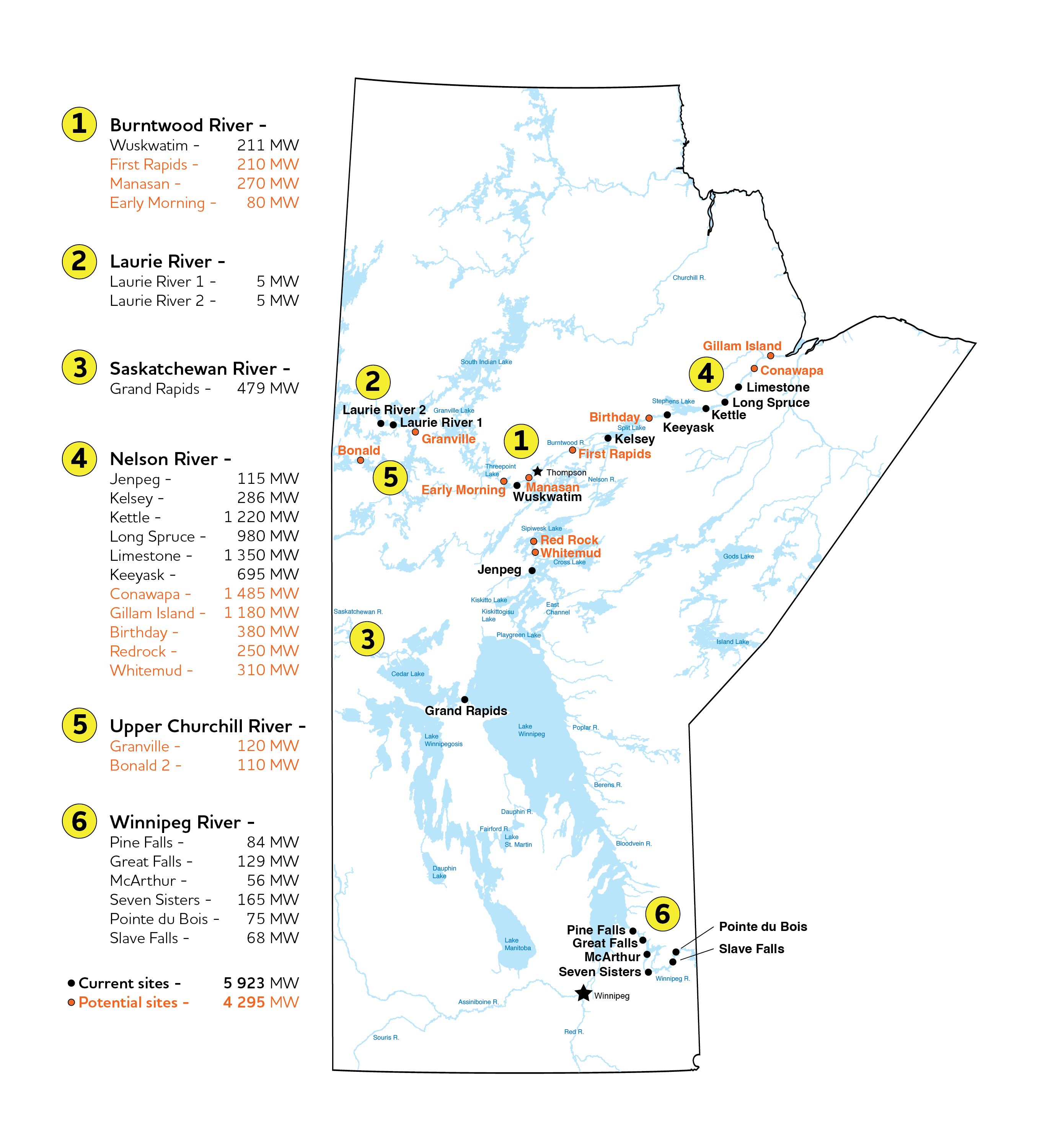
- Nearly all the electricity Manitoba Hydro produces each year is clean, renewable hydropower generated at 16 hydroelectric stations.
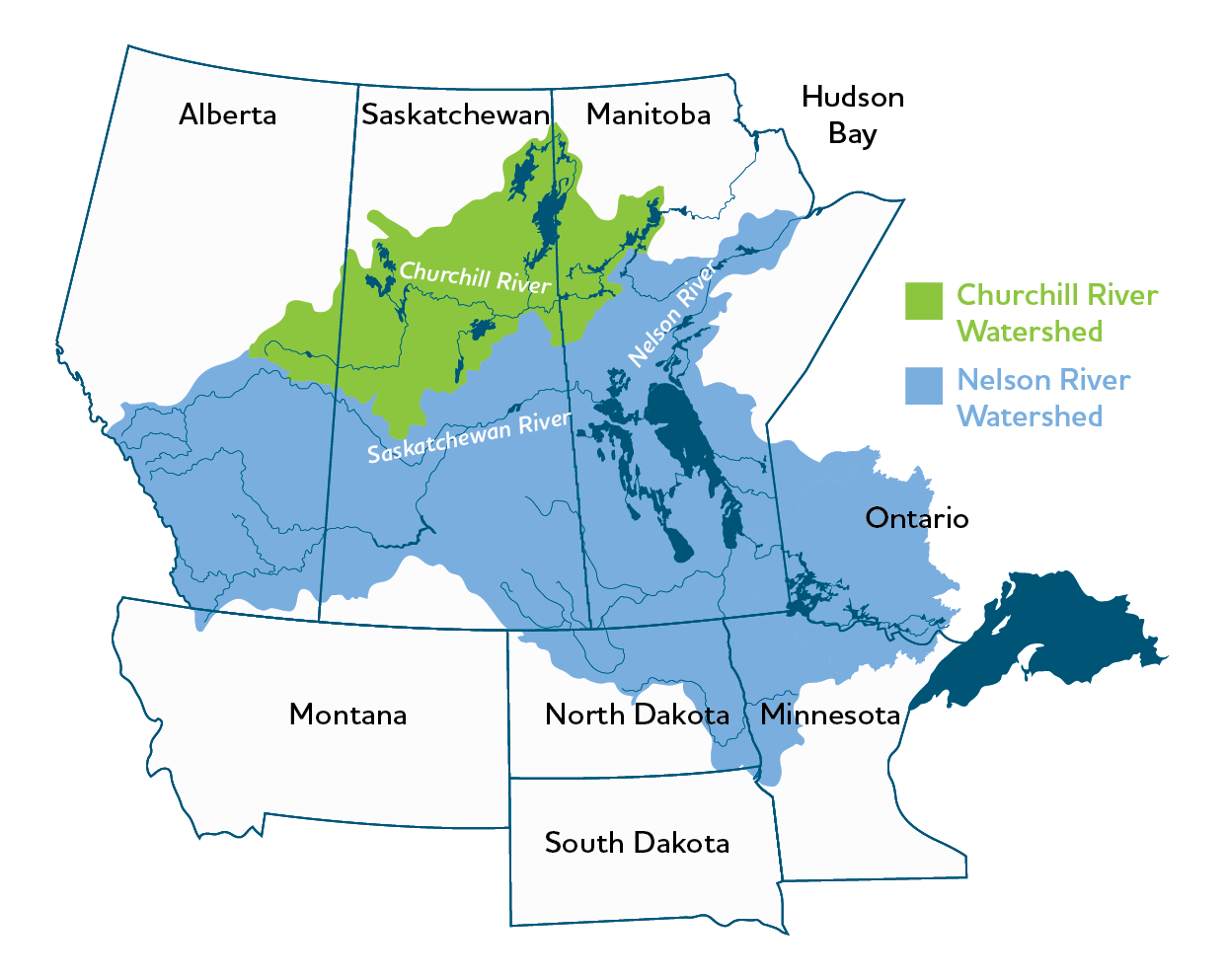
- Our system is fed by a massive watershed, helping to mitigate the risk of drought. Water is drawn from an area starting from near Lake Superior to the Rocky Mountains and into South Dakota.
- In addition to electricity sale agreements with U.S. utilities, we are a coordinating member of the Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO) which provides an opportunity to buy and sell energy in one of the largest electric energy markets in North America. We are also a market participant in the Southwest Power Pool (SPP).
- In a typical year, up to 25% of our production is exported to the U.S. through our transmission interconnections.
Manitoba Hydro - key facts (as of the 2021-22 fiscal year):
- 4,962 employees (over 20% Indigenous);
- 608,554 electricity customers;
- 293,256 natural gas customers;
- $3.04 billion in annual revenue;
- $31.14 billion in assets;
- 5,860 megawatts (MW) in generating capacity;
- 96% of our electricity is produced from renewable, low-emitting hydropower.
We are growing
Manitoba Hydro is well-positioned to help our utility customers further develop their own renewable energy sources. Hydroelectricity is a reliable source of generation that can store energy and respond to fluctuating demands for electricity. This flexibility makes it an excellent resource to complement the development of variable wind and solar resources.
Hydropower from Manitoba can also be an excellent source of firm base-load renewable energy.
- The 695 MW Keeyask Generating Station saw all seven units enter service in 2022, providing a new long-term source of renewable, virtually carbon-free energy.
- A new high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission line – Bipole III – entered service in the summer of 2018. Capable of carrying 2,000 MW, Bipole III significantly enhances our system reliability and increases capacity to transport electricity from generating stations in the north to southern Manitoba.
- The 500-kV Manitoba–Minnesota Transmission Project connects to the Great Northern Transmission Line and went into service in 2020. The project increased transmission capability for export to the MISO region by approximately 50%, while doubling import capability.
- The 230-kV Birtle Transmission Project went into service in 2021 and nearly doubled export capability to Saskatchewan in Canada. Beyond Keeyask, Manitoba Hydro has approximately 4,300 MW of undeveloped hydropower capacity.
Our transmission interconnections
Manitoba Hydro’s major export market is with the Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO), served by five transmission lines, the first built in 1970, the newest completed in 2020.
Besides delivering non-emitting, renewable hydropower, interconnections offer customers on either side of the border more options to maintain sufficient, reliable electricity supply, including:
- Sharing generation contingency reserves
Power system operators can pool their resources to cover loss of supply over the entire interconnected system, resulting in considerable cost savings. Manitoba Hydro currently has a contingency reserve sharing agreement with MISO. - Utilizing generation capacity more efficiently
The sharing of electricity resources enables both countries to maximize the efficiency of their generation resources when meeting their system peak loads. Where U.S. demand is generally highest in summer, Canada’s is generally highest in winter. Sharing capacity results in reduced overall capital investment requirements.
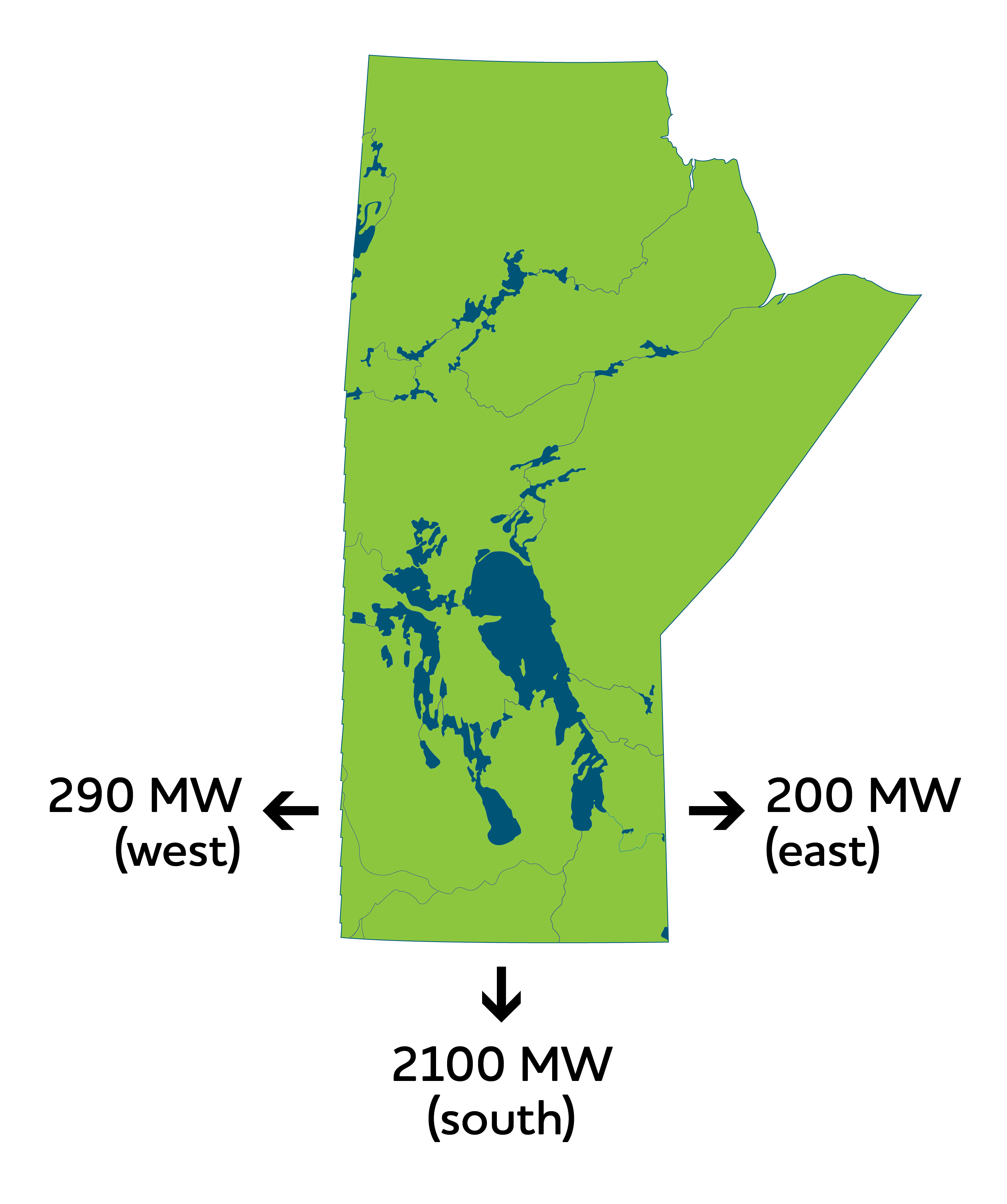
Manitoba Hydro transmission interconnections
Physically interconnected to:
- Minnesota
- 2-500 kV
- 1-230 kV
- North Dakota
- 2-230 kV
- Saskatchewan
- 4-230 kV
- 2-115 kV
- Ontario
- 2-230 kV